As a SEO rank tracking service, one of the most common support questions we receive is, “My rankings are not accurate.” This usually happens when users see a different ranking when they manually check the rankings of keywords they’re monitoring in their rank tracking tool.
Not knowing how Google and other search engines work and why they may give you results that are inconsistent with your keyword rank tracking tools can make you feel confused. You may find yourself not trusting the tool.
However, it is not necessarily the tool’s fault.
In this article, we’ll go through the misconceptions and misunderstandings of how search engines and localized results work - as well as what can be done about it.
Learning these concepts will prepare you to make the right decisions when optimizing a website and focusing on the most important aspect of your business - growth.
As an experienced, goal-oriented marketer, you should understand the SEO process and why you shouldn’t panic and confuse yourself, but instead focus on bringing the desired results to the business you’re optimizing.
How Does Google Work?
Google is everywhere. In order for such a comprehensive and giant organism to work effectively and find search results in under 50 milliseconds, the architecture of the system must be designed to provide different “access points” spread out across our planet. We call them data centers.

Located in different places across the world, data centers share over 10,000 servers, and some continents have several of them. They are needed to get the work done and deliver data quickly to the users around them, but they come with certain downsides.
Firstly, the data is not consistent between those data centers at all times, and secondly, the data is constantly being recalculated and synchronized. The web is always changing, which means that Google’s spiders have to keep “crawling” websites, indexing them, and sending the updates back to the servers.
What does it mean?
Someone in London searches for abs fitness guide. Google looks up their location and serves the request from the closest data center in Europe.
Someone in New York does the exact same search at the same time: abs fitness guide. In this case, Google sends them to the closest data center in North America.
So what happens here?
The data between those two data centers is not synchronized as a whole at all times, and for the same two keyword queries, people accessing different data centers would get different results.
Why and how, you might wonder? Because there are certain limitations and tradeoffs that engineers have to adhere to in order to make this system work effectively. The data is constantly being synchronized between data centers, and it has to be done in parts. In terms of Google, the order of results for each particular keyword is constantly recalculated as new data becomes available or updated.
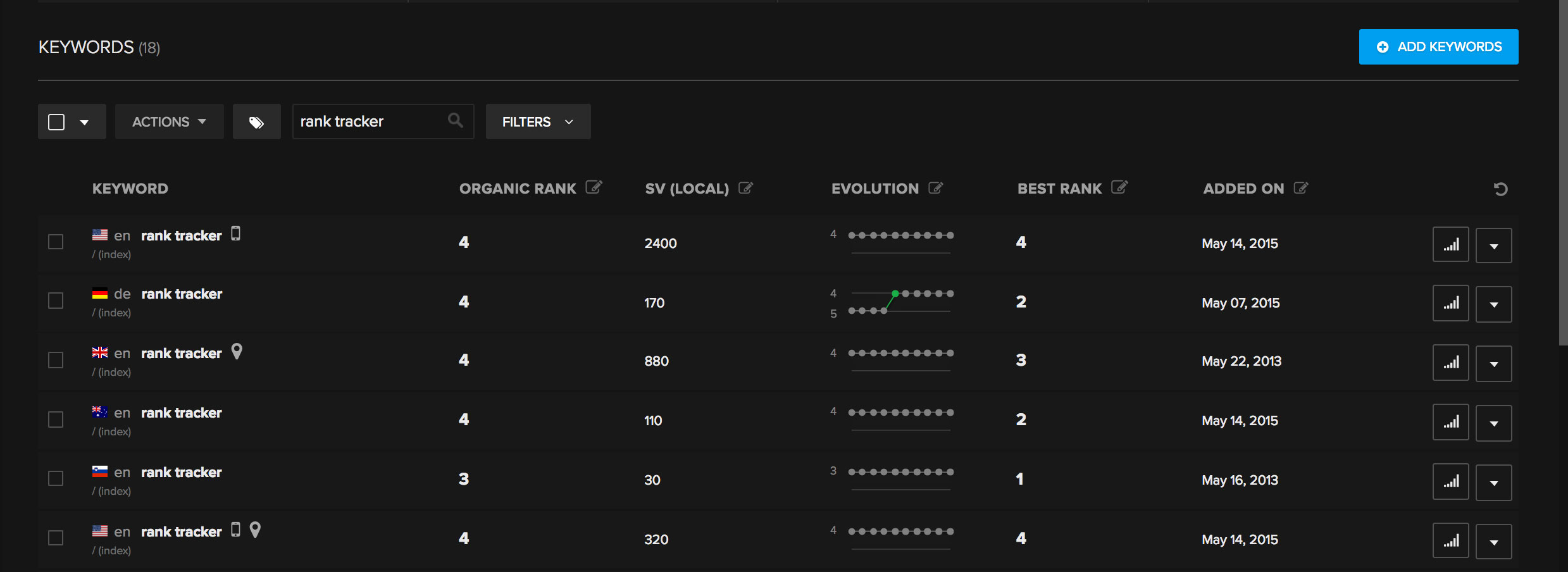
A search request triggered the next second would provide different results than the previous one, and it’s ok.
As you see, this is not a user’s or tracker’s problem; this is just how search engines work, and there is no way around it. While the results are flexible and unpredictable, there are certain rules to know about, and that knowledge will help us understand fluctuating search results.
This kind of phenomena is less likely to happen with general keywords - so called keywords with high search volume - such as tax, shoes, marketing, insurance, etc. and is more likely to happen on long-tailed keywords.
This makes us understand that when we observe this kind of behavior, it is likely due to instability of your website or the whole niche of a certain keyword.
This means that it’s more likely to happen with new websites than with well-established ones - those with rich backlink portfolios and greater age.
What can we learn from this?
Lesson 1: The more our website grows (read: gets older and receives more backlinks), the more it becomes stable in search engine result pages (SERP).
Lesson 2: Do not panic when you see different results for the same keyword. It’s normal. If you want to see a bigger picture, you can track the same keyword from multiple locations, for example, from different continents.
What’s the deal with local rankings?
We can split all search engine queries into two categories: global searches and local searches.
Global searches are those when we are looking for certain information, products, or services regardless of location. Local searches are those when we are searching for certain information in a specific geographical area.
Google, as well as other search engines, is equipped with its gigantic army of programmers to handle those situations with little risk to accuracy.
How does it work?
First, when you visit google.com, it tries to determine your current geographical location using location sharing services (if you enabled them), your https://www.lifewire.com/what-is-an-ip-address-2625920, or both.
What does it mean?
The localized search results shown to you depend on your location.
Google knows what keywords are expected to provide local results to the user. For example, restaurant, golf place, sake bar, and law firm are more likely to display local results than red nike shoes or heartburn symptoms.
Therefore, if you search for best sushi in London or New York, it will provide you with suggestions according to your current location.
So how accurate are the local results?
Sometimes your location cannot be determined with complete accuracy for two reasons: either location sharing isn’t enabled in your browser, or Google is unable to ascertain your location via your IP address.
This means that if we’re tracking local results for a precise location, we cannot assume that Google will detect the same location on our local computer or smartphone, even if we’re located in the same area.
You can read more about this in our ultimate guide to local tracking.
What else affects accuracy?
You could be forgiven for thinking what we’ve mentioned so far is enough to understand the tracking game. There are more things that come into play, and we will briefly explain them here for you to master this fully.
Personalization
Every time you visit Google from the same browser (with the same cookies or history) or while being logged in to Gmail, Google adjusts the results according to your browser history. It’s not a big deal, and you can easily bypass that by opening a browser in privacy mode, or Incognito mode.
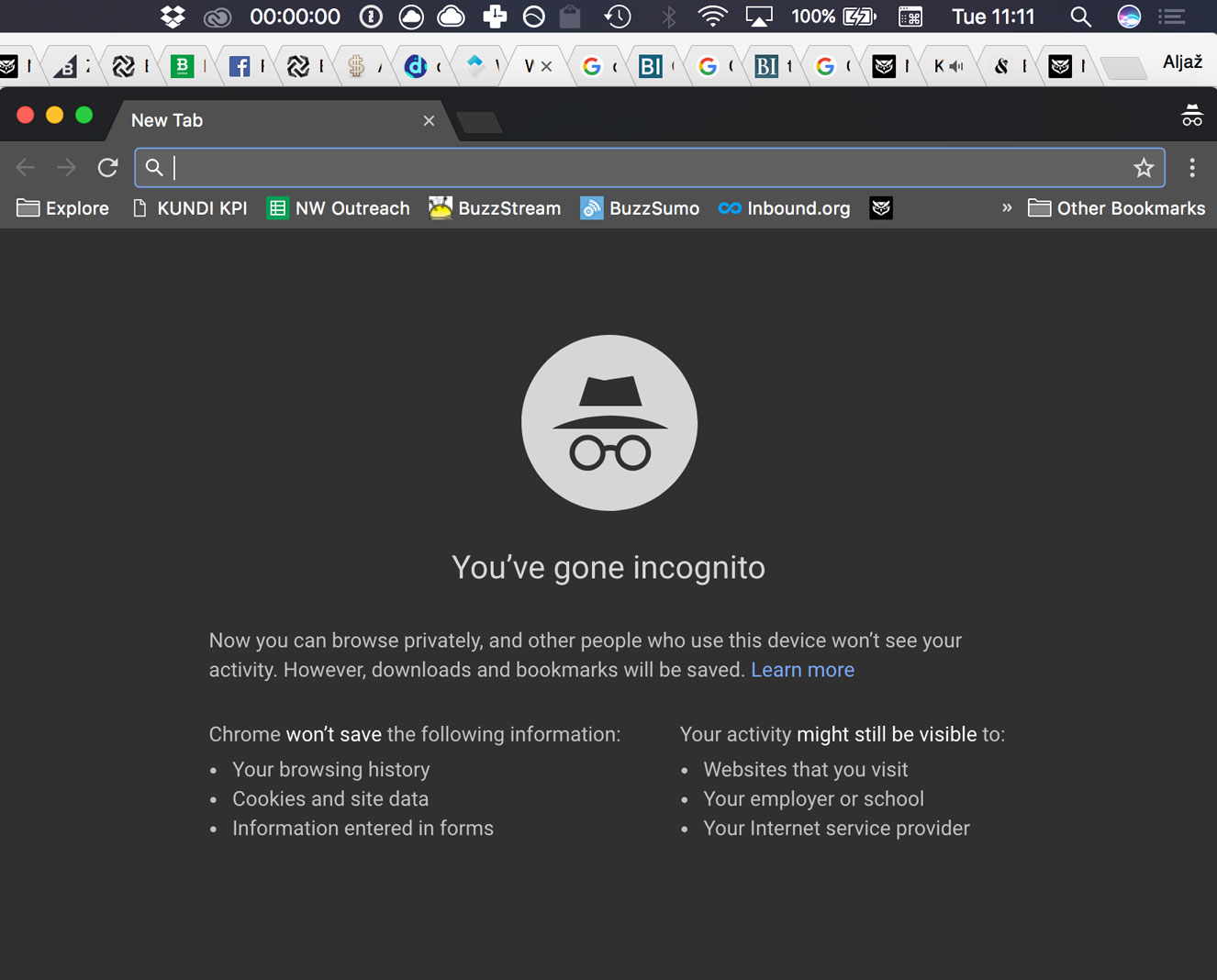
Using a browser in privacy mode will just disable history and cache - any data that could be stored from your browsing history and affect the personalization of the results, - so it makes your local results less “biased.”
Results per page setting
By default, Google shows 10 results per page, but you can configure it to show more results at once - up to 100. Most of the trackers when retrieving results from Google or other search engines will try to get 100 results at once in order to save resources (they need to do 1 request instead of 10), but there comes the price with it.
When requesting 100 results at once, Google merges results from the same domain. This means that it is highly possible that results will be in a different order when using the “100 results per page” setting instead of the default “10 results per page.”
Most users are unaware of that, and still, it sometimes causes great confusion if they try to search for their results manually and compare them to their tracker’s rankings.
With Nightwatch, we are using a special approach when handling this situation. To reduce the anomalies in the data that come because of this behavior, we will first request 100 results, and if the tracked result is found within the top 20 positions, we will request the first 2 pages separately by 10 results per page settings in order to fine-tune the accuracy of the most significant positions - where it’s crucial to provide accurate numbers to be able to calculate trends and predictions more accurately).
What is Google Dance and how does it affect my rankings?
Google Dance once referred to a time when major updates to its algorithms were implemented, which occurred about 10 times a year. Substantial changes in search results were noticeable because they “danced” around. It didn’t all happen simultaneously, though, and would take several days to complete the entire update.
For anyone in the search engine optimization industry, this is a period of significance, though maybe not affection. Sometimes pages would be completely dropped from the index for a day or more. Understandably, this was panic-inducing for some people. Eventually, the dropped websites would find themselves back in the index, maybe even with better rankings than before, and all was well on the world wide web again.
Things have changed since then. Updates are weekly, considerably less startling, and usually contain minor changes to the algorithm and index.
There is still a little dance, though. During each month, minor changes occur in rankings because Google’s bot is always finding, updating, and filtering website data. The bot may have found a new website or discovered a defunct one, both situations requiring updates to the results. The bot will revisit every website, analyze all the sites linking to it, linking out from it, and how worthwhile these links are.
So how do I check my rankings?
So, we finally came to the chapter where we should answer the most important question: knowing all presented in this article, can I check rankings from my computer or smartphone accurately? The answer is no… and yes.
No, because it is practically impossible to simulate a precise location search on your local computer, which Nightwatch does provide - as well as some other advanced rank trackers. This requires you to fake the geographical location to a specific area supported by Google, which affects search results.
There is no easy way to configure this on your local computer - the only way you could do it is if you were located in the area (which is detected the same as the precise location configured in Nightwatch), but it is just a half of the deal.
Still, if you want to check your rankings manually, here is what you should follow for more accurate results:
- Use browser in privacy (Incognito) mode,
- Use a proxy or VPN with the exact location as the tracked location of your keyword,
- In Google, configure the same language as of your tracked keyword,
- Experiment with “10 results per page” and “100 results per page.”
In addition, you could try using location faking tools, for example, Google Adwords Ad Preview or I Search From. Note that the accuracy isn’t guaranteed, and the results are quite approximate.
Still, it is highly possible that you won’t be seeing the same rankings as in the tracker, and it’s ok.
You can experiment with adding the same keyword tracked on different locations - this approach is explained in our ultimate guide to tracking local rankings.
Conclusion
With all things considered, it is not as easy to simulate unbiased search query from your computer, but worry not: we got you.
If you manually search for your keywords from time to time, you should know you can’t rely on the results completely.
While Nightwatch allows the best possible accuracy knowing all the factors that affect the results, you can still apply practices presented in this article to understand and cope with certain situations that occasionally come with search engine’s Pandora box.
